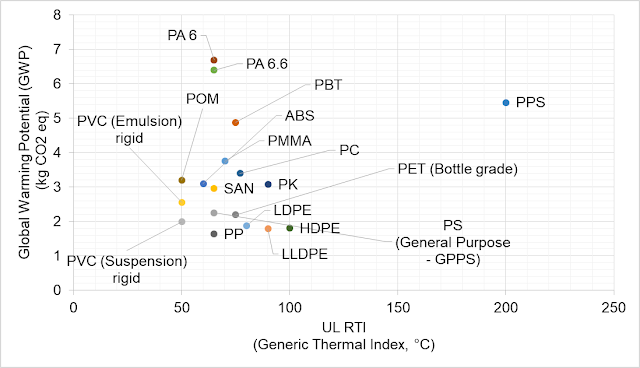
|
| Example for recycling - LDPE (REC80) plastic bag: it is made 80% out of old PE sheets. |
Hello and
welcome to a new blog post. Today we discuss sustainability in the plastics
industry, starting with an overview and definitions.
Please check
out my video on this topic too, accompanying this blog post:
What is Environmental Sustainability?
According to Michel Biron [1], environmental sustainability is a tripod
based on environmental requirements, economic growth (creating sustainable products
which are efficient, cost efficient, and beneficial), and social progress
(including fair labor standards).
 |
| Sustainability: a tripod based on environmental requirements, economic growth |
In business, sustainably is more and more defined as a goal, which needs to
be reached in a certain amount of time. In addition, the concept of
sustainability can be extended to the health impact of products and materials.
In this concept, unsustainable solutions can be easier identified than
sustainable solutions, since the product or material negatively affects human
(or animal or plant) health. Linked to sustainability in the industrial
surrounding is economic sustainability, which refers to the ability of a
company to survive in the long-term. Avoiding higher costs is one of the base
rules for plastics manufacturers and processors.
What does sustainability mean for an industrial company?
On the one hand, there are direct activities such as manufacturing
operations that are under direct control of the business and allows
implementing directly measurable sustainability goals. On the other hand, there
are indirect activities connected to the upstream and downstream of the
business supply chain such as freight costs, and energy production. The
indirect activities can result in a major footprint to a business and can be
even much larger than the direct one.
Circular Economy
In our current linear economy setup we produce, use and dispose of
products, putting pressure on the availability of natural and fossil resources
as well as pollution. Circular economy puts the emphasis on producing goods out
of recovered materials, using them and recycling them to gain the maximum out
of the product after the usage phase. All over, the circular economy is an essential
piece for better sustainability.
Plastic manufacturing and processing companies are increasing their efforts
to enable a plastics circular economy. Creating bio- and recycled based
products supports this effort. Advanced plastics recycling, which is using
chemical or molecular recycling is speeding up too. Technological, economic,
and policy uncertainties are the biggest challenges for plastics companies to
move forward in this area. Integrated energy and plastics company OMV created
with ReOil® a technology which converts post-consumer and post-industrial
plastics to synthetic crude oil and petrochemical feedstock which can be used
for virgin plastics production again [3].
There are more and more initiatives such as Cyclyx drive up recycling rates
[2]. Currently, only about 10% of plastics are recycled.
Sustainability in the Plastics Industry – where to put the focus?
Biron [1] identified six major areas to put the focus on when implementing
a sustainability concept. Sustainable design challenges designers to find the
best balance between durability, performance, energy saving, carbon footprint
reduction, and recycling. There will be questions such as “Should I use natural
sourced polymers which consume water and fertilizers or fossil based polymers which
consume crude oil?” This brings us to the second area: renewable polymers. In
order for bio-based polymers to succeed, their raw material must not compete
with food, use less net water, be energy efficient, together with using
renewable energy and emit less greenhouse gases. In addition, they should be
less polluting and lead to a smaller carbon footprint during the whole life
cycle.
Sustainable manufacturing as the third area covers a process step
integration to save energy, focusing on energy efficiency and renewable energy.
Are four, the use phase, shows the full potential of plastics. From insulation
foams which save energy for heating and cooling devices, houses, and many more,
to light weighting in automotive and other transport vehicles. Packaging is a
major contributor since it enables to extend the lifetime of fresh food.
Area 5 is waste management, including repairing, reusing and recycling. In
addition, the sixth area described the economic involvements. Sustainably
solutions may lead to an economic advantage. However, it can also result in
extra costs, which will challenge the customer to accept them. Therefore, the
challenge is to offer sustainability solutions at competitive pricing in the
end.
Summary
Overall, creating a sustainability concept is a step-by-step progress
toward the best possible sustainability in your company and we see more and
more promising approaches by different companies in the year 2022. I am curious
how this will evolve beyond 2022.
Thanks for reading and #findoutaboutplastics
Herwig Juster
Check out my other posts on environmental impact of polymere here:
Interested to talk with me about your plastic selection, sustainability, and part design needs - here you can contact me
Literature:
[1] M. Biron: An overview of sustainability and
plastics, Elsevier, 2020
[3] https://www.omv.com/en/sustainability/climate-protection/reoil