Hello
and welcome to a new blog post. Today I present to you selected properties of
natural fiber based polymer compounds as part of our design data for plastic
engineering series.
Which
natural fibers can be used and why to replace e-glass with them?
The
use of natural fibers represents a sustainable alternative to synthetic glass
and carbon fibers. They can be used in applications ranging from automotive,
aeronautics to building and construction. Natural fibers can be plant, animal,
and mineral based. In this post, we focus only on plant based fibers as
reinforcement. The most important plant based fibers (cellulose) include
cotton, flax, hemp, jute, pineapple, abaca, wood, wheat, rice, bamboo, and
esparto. Among the animal fibers are lamb’s wool, goat hair, angora wool, and
cashmere. Mineral fibers are fibrous brucite and wollastonite.
Recycling
of glass and carbon fibers is still high energy consuming. Table 1 shows the
environmental parameters (production of 1 kg of fibers [5]) of hemp and glass
fibers. In all three categories, hemp fibers represent a sustainable
alternative to glass fibers.
 |
| Table 1: environmental parameters (production of 1 kg of fibers [5]) of hemp and glass fibers |
Properties
of fibers
Before
deciding to replace glass fibers with natural fibers, a look at the mechanical
properties of natural fibers is important. This will later enable a better
material formulation and material selection.
Figure
1 and 2 compares the mechanical properties of glass with those of jute, flax,
hemp, and cotton. It can be shown that the tensile modulus of flex and hamp is
with 70 GPa in the range of the glass tensile modulus.
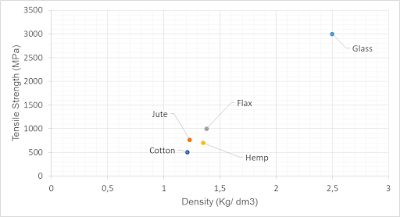 |
| Figure 1: Tensile strength vs. density of different natural fibers and glass fiber |
 |
| Figure 2: Tensile modulus vs. density of different natural fibers and glass fiber |
For
formulating plastic compounds using natural fibers, thermal processing
properties must be in the suitable range of the fibers. Polyethylene (PE) and
Polypropylene (PP) base polymers are good examples for such a suitability and
our examples will be based on a PP copolymer.
Figure
3 presents the mechanical properties of PP based natural fiber compounds (six
different fibers; always 35%) and compares them to a PP based glass fiber
compound (also 35%). Within the natural fiber compounds, mechanical values are
in a similar range. PP glass fiber reinforced compounds are double in tensile
modulus and tensile strength.
 |
| Figure 3: Tensile modulus vs. tensile strength of different PP compounds with natural fiber reinforcement and PP with glass fiber reinforcement |
Conclusions
Natural
fiber based compounds allow a weight saving in the range of 10 -30%. Most used
fibers are hemp, jute, and flax. Hemp fiber production is almost pesticide
free. Additionally, hemp fibers are hydrophilic and proper drying must be done
prior to compounding. In terms of performance, natural fiber compounds can be
used in automotive interior applications (door panels, seat backs paneling),
together with exterior applications (bumpers, spoilers). In building and
construction, such compounds can be found in roof panels and insulations.
Thanks
for reading and #findoutaboutplastics
Herwig
Juster
Interested to talk with me about your plastic selection, sustainability, and part design needs - here you can contact me
Literature:
[1]
WIS Polymer-Wissenmatrix; https://www.advanced-compounding.com/de/polywood-pp.html
[3] https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2019.00226/full#B95
[4] https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03153829/document
[5]
Shahzad, 2011: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0021998311413623

No comments:
Post a Comment