Hello and welcome to a new blog post in which we discuss if there are PTFE free alternatives for lubrication.
Why replace PTFE in friction and wear materials?
In the regulation "EU 2019/1021" of the European Union, Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) are already listed and restricted in use. Further restrictions are under discussion and alternatives to replace materials such as PTFE gain traction.
PTFE is due to its chemical composition an extremely stable polymer with a low static and dynamic coefficient of friction. Using it in small amounts as additive for friction and wear materials is advantageous. Also, self-lubrication properties are possible. On the other hand, the fluorine is subject to more stringent regulation and the PTFE containing compounds are more aggressive during processing (mould deposits, corrosion and fumes).
What are PTFE free alternatives for friction and wear compounds?
Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene UHMW-PE is known for its high abrasion resistance. By using UHMW-PE dispersed in a base polymer similar coefficient of friction values can be achieved.
There are several methods to estimate the material wear resistance. The sand slurry test (ISO 15527) is a good test to estimate the wear resistance of thermoplastics. In this test, the specimen is rotated 200 - 2400 RPM for 3 hours inside a box which contains the abrasive material (aluminum oxide or silica). The loss of mass is calculated after the test and compared to other material specimens. UHMW-PE has a coefficient of friction of 0.25, which is higher than the coefficient of friction of PTFE (0.1), however the wear resistance is 8 times better than PTFE.
Apart from the sand slurry test, there is the taber abrasion test. The specimen is exposed to an abrasive wheel for 1000 cycles and weight loss of a material is measured. Also in this test, UHMW-PE performs well and outperforms PTFE (Table 1).
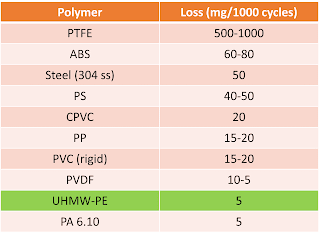 |
| Table 1: Taber abrasion test - results of different polymers and steel |
What are some inherently wear-resistant polymers?
Apart from UHMWPE, there are polymers which are inherently wear-resistant:
-Polyketone (POK)
-Polyoxymethylene (POM)
-Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)
-Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
-Polyamide (PA)
-Polyamide-Imide (PAI)
-Polybenzimidazole (PBI)
In conclusion, from an polymer material selection point of view, UHMW-PE is an alternative material for applications that need excellent sliding properties as well as excellent wear resistance. Downside is that UHMWPE cannot be used for high temperatures as it is the case with PTFE. For high temperatures, PEEK can be a good, however more expensive alternative. Furthermore, flame retardant properties can be achieved by mixing UHMW-PE (wt 80%) with PTFE (wt 20%).
Another PTFE filler alternative is Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) which can offer a fluorine- and micro plastic-free replacement. The very good lubricating properties of hBN come from its crystal structure. We discussed this in detail with Michaela Schopp - Product Manager at Henze BNP AG in this guest interview here.
Recently i received good feedback from one of our community members regarding an additional filler to replace PTFE: Molybdenum Disulphide (moly filler) - MoS2.
Adding moly filler as an additive to your polymer compound, low coefficient of friction, abrasion and wear resistance, as well as excellent low and high temperature properties can be achieved. Furthermore, molybdenum disulphide can be used to reduce the impact of other additives, such as glass fibers, on the tribology.
Thank you for reading and #findoutaboutplastics
Greetings,
Herwig
Interested in my monthly blog posts – then subscribe here and receive my high performance polymers knowledge matrix.
!NEW! Ultra and High Performance Polymer Selection - new online course coming soon - join the waiting list
Literature:
[1] https://www.umco.de/de/blog/artikel/PFAS-Einschraenkungen.html
[2] http://www.sugison.com/div-eng/_shared/files/PE-UHMW%20compare%20to%20PTFE.pdf
[3] https://www.plastix-world.com/ptfe-free-self-lubricating-compound/
[4] https://www.corzan.com/en-us/piping-systems/specification/abrasion-resistance
[5] https://www.brad-kem.com/moly-filler-for-plastics/#:~:text=Plastics%20Manufacturers%20make%20moly%20filled,Abrasion%20and%20wear%20resistance

No comments:
Post a Comment